We all know we need calcium for strong teeth and bones, but did you know that calcium is also needed for the life preserving functions of muscle contraction, (including the heart) blood clotting, nerve function and the release of certain hormones and enzymes?
Because calcium is necessary for the maintenance of life, it is leached from the bones if the amount in the blood in insufficient for these life preserving functions. You can still live without brittle bones, but you can’t live without a heart beat, so the body very cleverly prioritises the function that calcium is directed to. If there’s insufficient calcium circulating in the blood, the body takes it from it’s storage cells, the bones and teeth.
Calcium and Cola Drinks
As an aside, a highly acidic diet can cause calcium to be leached from the bones. Your body will act to maintain a blood pH of 7.4. If you have a highly acid diet, your body will draw down on stored mineral salts, including calcium, which act as a buffer to the acid and work to restore blood to a pH of 7.4. Lots of things can cause a drop in blood pH (ie a rise in acidity) including cola drinks. Therefore chronic use of cola (and to a lesser extent other soft drinks) can lead to brittle bones. And that includes the diet varieties as well! You can flush the acid away with water, but for every can of cola you drink, you’d need to take in 15-25 times that amount in water. (Then spend an awful lot of time in the loo).
Calcium and Muscle Function
Here’s the interesting bit for we exercise types. You should be sure to have enough calcium in your diet, and good gut health, to be able to contract your muscles.Below is a very abridged and simplified version of how calcium acts in skeletal muscle contraction.
- The brain sends an electrical impulse to the muscle. A lot of biomechanical reactions need to take place for the message to get to the muscle safely, but, amazingly, in most cases it does.
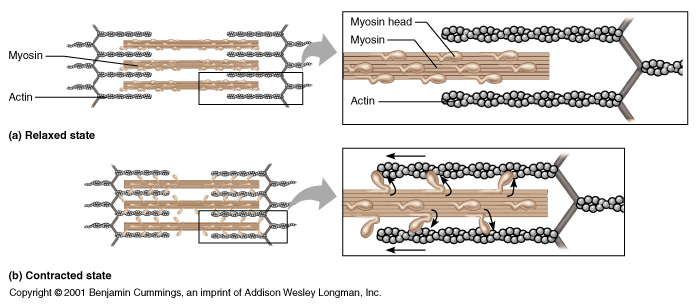
- After receiving the message, the muscle shortens. This action is explained by what is know as the sliding filament theory.
- Within a muscle fibre, there are two different types of filaments, actin and myosin. These filaments are layered one on top of the other, as in the picture below.
- When the right biochemical reactions take place, cross bridges form between the actin and myosin filamines, and the actin gets pulled by the myosin, so the two filaments are pulled closer together and the muscle shortens.
For all of this to happen, calcium is needed to “unlock” the active sites on the actin filament which the myosin attaches to. The myosin heads continue to reattach further and further along the actin, causing a more forceful contraction of the muscle.
The muscle stops contracting when the release of calcium ions stop. You need adequate magnesium for this, but that’s a biochemistry lesson for another day.
Suffice is to say, if you want to run fast, make sure you have enough calcium in your diet.
How Much Calcium?
Check out some calcium rich foods here
Reference: https://www.osteoporosis.org.au/about-osteoporosis